How community virtual classes can bridge learning gap, address inequality

How to Address Inequities in Remote Learning Online learning, Online
These inequalities in countries' ability to offer online remote learning may have carried over into inequalities in student engagement. As referenced earlier, synchronous activities (usually facilitated by online interaction) were one mechanism to keep students engaged even outside the classroom (Muñoz-Najar et al., 2021 ).

Remote Learning Exacerbates Inequality. Here’s How We Must Support the
An industry study found that "total online spending in May 2020 reached $82.5 billion, up 77% from May of 2019" and those numbers almost surely will increase in coming months as people.

The Digital Divide and COVID19 Teachers' Perceptions of Inequities in
Inequity in remote learning. While remote learning helped manage the COVID-19 spread, many families were not equipped for this type of at-home learning. Many lower-income households do not have at-home technology required for virtual learning and guardians of young students have to balance overseeing virtual learning with their own.

OPINION We can — and must — use distance learning to address
An found that "total online spending in May 2020 reached $82.5 billion, up 77% from May of 2019" and those numbers almost surely will increase in coming months as people appreciate the.

Remote Learning Plan Triangle Inequality Theorem OER Commons
Results of a survey conducted in April with parents in Texas, New York, California, and Washington show that one in five Black parents received little to no information from their school about remote learning resources during the pandemic. 18 Responses from a survey conducted in March show that 25% of Black youth connected with teachers less.

Remote Learning Boardworks Education
The COVID-19 pandemic ushered in a dramatic shift to online learning for K-12 public schools, requiring school districts to address inequities that surfaced in the remote learning model. This paper includes the findings of the second study of a multi-year research project exploring the intersection of technology and educational inequities through the pandemic. As the pandemic waned.

Remote Learning Expectations Chart Mini lessons, Learning, Learning
Remote learning turned spotlight on gaps in resources, funding, and tech — but also offered hints on reform. "Unequal" is a multipart series highlighting the work of Harvard faculty, staff, students, alumni, and researchers on issues of race and inequality across the U.S. This part looks at how the pandemic called attention to issues.
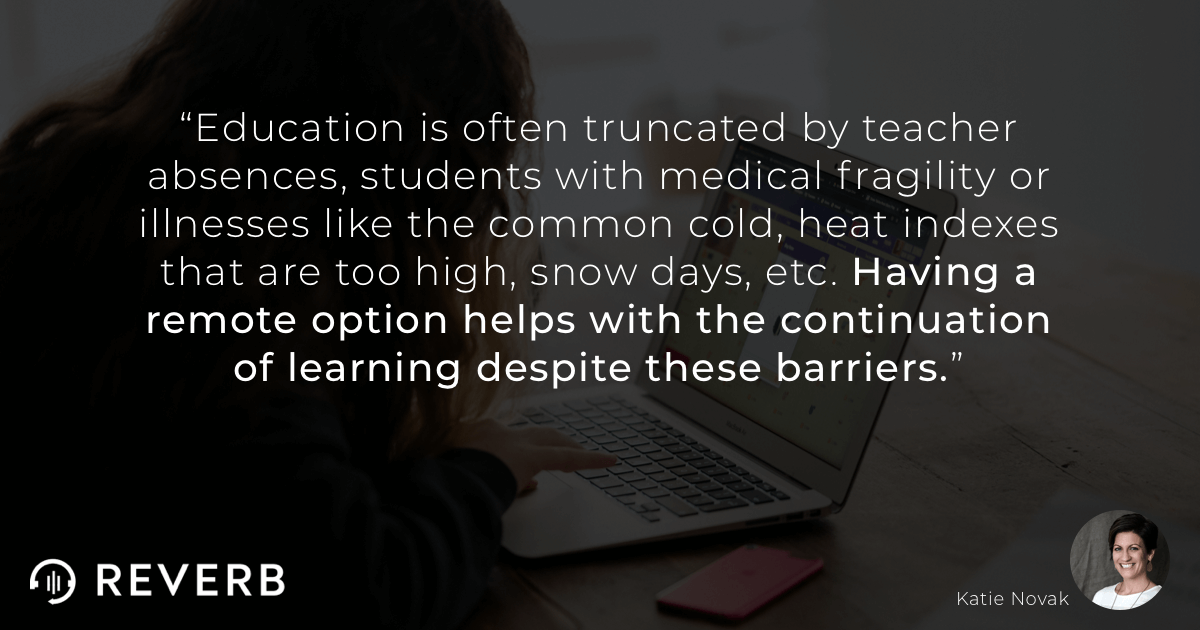
Minimizing Inequities in Remote Education Through Universal Design for
Background Remote learning, or synchronous or asynchronous instruction provided to students outside the classroom, was a common strategy used by schools to ensure learning continuity for their students when many school buildings were forced to shut down due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Differences in technology infrastructures, digital competencies of students and teachers, and home supports for.

The Evidence for Tutoring to Accelerate Learning and Address
Abrupt shifts to remote learning over the past two school years. socioeconomic, and other educational inequities. 1. Data collected before and during the COVID-19 pandemic have shown that in-person learning, on the whole, leads to better academic outcomes, greater levels of student engagement, higher rates of attendance, and better social.
:quality(70)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/tronc/RBN7TXMRGBCGBEHWU7G7NPCXJM.jpg)
Help students and working parents succeed during remote learning
Remote online learning also limited or curtailed student opportunities for socialization and nonacademic activities, the report said, causing many students to become disengaged or drop out of school.

Strategies in Addressing ICT Inequality in Remote Learning The
The Education Gap: Addressing Inequalities in Remote Learning. The COVID-19 pandemic has catalyzed a massive shift in education, with remote learning becoming the new norm for millions of students.

Infographic Remote Learning and The Resiliency of Educators
In this learning review, we will focus on how remote learning fell short with regard to the digital divide and what we can do to improve in subsequent terms. Remote learning exacerbated inequities in education, which existed well before the Spring of 2020. In 2012, The Atlantic article entitled "The Decline of the 'Great Equalizer.

How remote learning is making educational inequities worse USC
The messy transition to remote learning in America's K-12 education system as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic has been marked by glaring disparities among schools, according to nationally.

How community virtual classes can bridge learning gap, address inequality
8. One-third of schools reported plans to offer remote instruction to any student who wants it after the pandemic has passed. Schools that have been remote in 2020-2021 were more likely to be planning for remote options in future school years. Recommendations to address inequitable teaching and learning pathways include: 1.
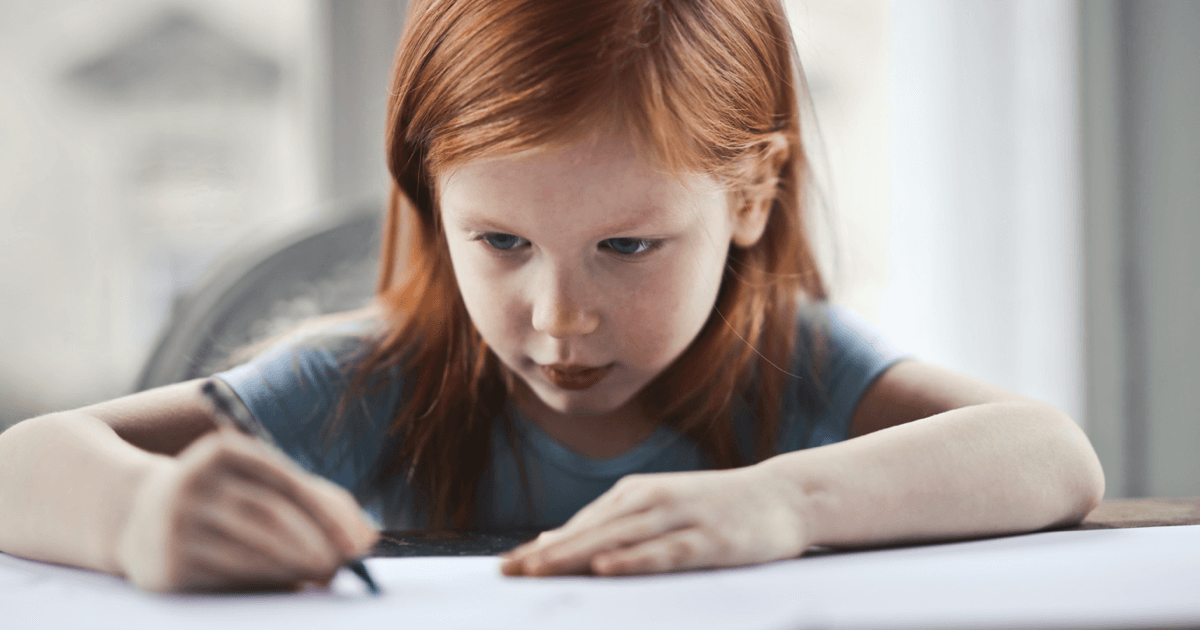

Minimizing Inequities in Remote Education Through Universal Design for
العربية. NEW YORK, 5 June 2020 - As nearly 1.2 billion [1] schoolchildren remain affected by school closures and as they grapple with the realities of remote learning in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic, UNICEF warns inherent inequalities in access to tools and technology threaten to deepen the global learning crisis.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/67461699/VOX_16_F.0.jpg)
How to do remote learning, explained by teachers and students Vox
In this paper, we argue that the COVID-19 pandemic will exacerbate existing racial wealth inequality, and specifically, that the switch to remote learning for K-12 students during the pandemic will reinforce educational disparities by race and ethnicity. Given the link between educational achievement and future income, pandemic-induced.